Conduction convection and radiation worksheet answer key – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of heat transfer as we delve into the intricacies of conduction, convection, and radiation. This comprehensive guide, meticulously crafted with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif, unveils the fundamental principles governing these phenomena, providing a solid foundation for understanding heat transfer in our everyday lives.
Through a seamless blend of theoretical explanations, practical examples, and insightful illustrations, this guide empowers readers to grasp the nuances of heat transfer, fostering a deeper appreciation for the underlying scientific principles that shape our world.
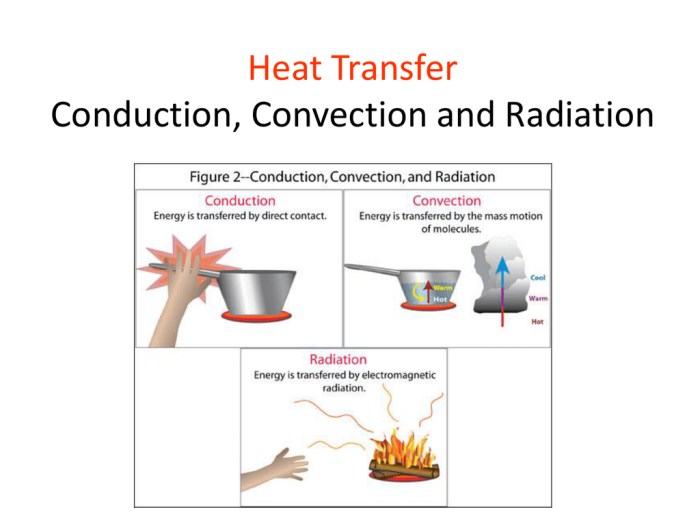
Conduction: Conduction Convection And Radiation Worksheet Answer Key
Conduction is the transfer of heat energy through direct contact between objects or substances. It occurs when molecules in a hotter object vibrate and collide with molecules in a cooler object, transferring their thermal energy.
Examples of conduction include:
- Touching a hot stove
- Melting ice on a warm surface
- Transferring heat through a metal spoon
| Heat Transfer Method | Mechanism | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct contact between objects | Touching a hot stove, melting ice on a warm surface |
| Convection | Transfer through fluid movement | Boiling water, wind cooling |
| Radiation | Transfer through electromagnetic waves | Sunlight warming the Earth, heat from a fireplace |
Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat energy through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). As a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler fluid sinks. This creates a convection current, which carries heat energy throughout the fluid.
Examples of convection include:
- Boiling water
- Wind cooling
- Heat rising from a fireplace
Diagram of Convection:

Radiation

Radiation is the transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, making radiation the only heat transfer method that can occur in space.
Examples of radiation include:
- Sunlight warming the Earth
- Heat from a fireplace
- Microwaves heating food
Types of Radiation:
- Infrared radiation
- Visible light
- Ultraviolet radiation
- X-rays
- Gamma rays
Worksheet Answer Key
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Define conduction. | Transfer of heat energy through direct contact between objects. | Conduction occurs when molecules in a hotter object vibrate and collide with molecules in a cooler object, transferring their thermal energy. |
| Give an example of conduction. | Touching a hot stove. | When you touch a hot stove, the heat energy from the stove is transferred to your hand through conduction. |
| Define convection. | Transfer of heat energy through the movement of fluids. | Convection occurs when a fluid is heated, becomes less dense, and rises, while cooler fluid sinks, creating a convection current. |
| Give an example of convection. | Boiling water. | When water is heated, the bottom layer of water becomes less dense and rises, while the cooler water sinks, creating a convection current that circulates the water and transfers heat throughout the pot. |
| Define radiation. | Transfer of heat energy through electromagnetic waves. | Radiation occurs when electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation or visible light, travel through a vacuum or through a medium such as air. |
| Give an example of radiation. | Sunlight warming the Earth. | Sunlight is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels through space and warms the Earth’s surface. |
FAQ Explained
What is the primary difference between conduction and convection?
Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact between objects, while convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid (liquid or gas).
Can radiation occur in a vacuum?
Yes, radiation can occur in a vacuum because it does not require a medium for propagation.
What is the most efficient method of heat transfer?
Conduction is generally the most efficient method of heat transfer, followed by convection and then radiation.
