Embark on an educational journey with independent practice Punnett squares answers, a fundamental tool in genetics. These squares empower us to predict the potential genotypes and phenotypes of offspring, unraveling the mysteries of heredity. Delve into the fascinating world of Punnett squares and unlock the secrets of genetic inheritance.
Unveiling the intricacies of Punnett squares, we explore their construction, application, and significance in understanding genetic traits. Through step-by-step guidance and real-world examples, this discourse illuminates the power of Punnett squares in unraveling the complexities of genetic inheritance.
Punnett Square Basics

A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from parents with known genotypes.
For example, consider a simple Mendelian trait like eye color, where brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b). A Punnett square for this trait would look like this:
| B | B | |
| b | Bb | Bb |
| b | Bb | Bb |
The genotypes of the offspring are BB, Bb, Bb, and bb. The phenotypes are brown eyes (BB and Bb) and blue eyes (bb).
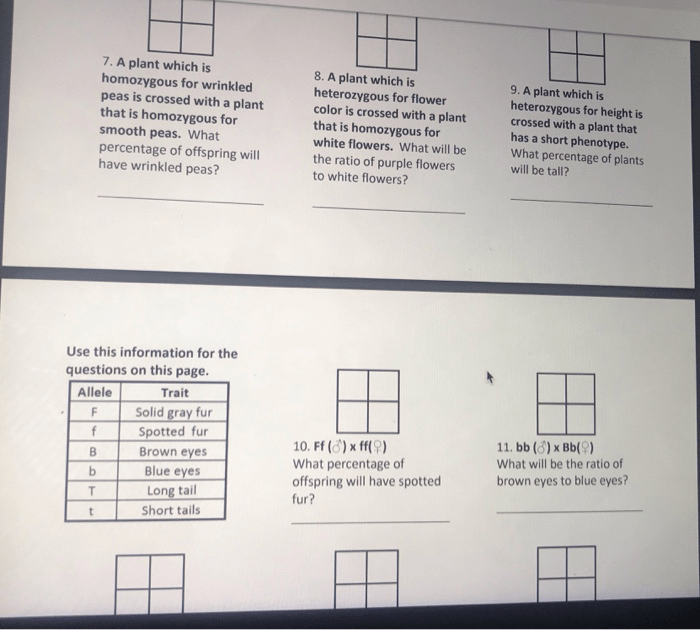
Independent Practice Punnett Squares: Independent Practice Punnett Squares Answers

To create a Punnett square for an independent practice, follow these steps:
- Write the genotypes of the parents along the top and side of the square.
- Fill in the squares with the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
For example, consider a cross between two heterozygous pea plants (Aa x Aa). The Punnett square would look like this:
| A | a | |
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
The genotypes of the offspring are AA, Aa, Aa, and aa. The phenotypes are tall plants (AA and Aa) and short plants (aa).
Punnett Square Applications

Punnett squares are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Genetic counseling: Punnett squares can be used to predict the risk of a couple passing on a genetic disorder to their children.
- Breeding: Punnett squares can be used to predict the traits of offspring in breeding programs.
- Research and education: Punnett squares are used in research to study the inheritance of traits and in education to teach students about genetics.
Advanced Punnett Squares
There are several types of Punnett squares, including:
| Type | Description |
| Monohybrid | Predicts the inheritance of a single trait. |
| Dihybrid | Predicts the inheritance of two traits. |
| Incomplete dominance | Predicts the inheritance of traits that are not completely dominant or recessive. |
| Codominance | Predicts the inheritance of traits that are both dominant. |
Punnett squares can also be used to analyze traits with multiple alleles. For example, the ABO blood group system has three alleles: A, B, and O. A Punnett square for this system would look like this:
| A | B | O | |
| A | AA | AO | AO |
| B | AO | BB | BO |
| O | AO | BO | OO |
The genotypes of the offspring are AA, AO, AO, BB, BO, BO, and OO. The phenotypes are blood type A (AA and AO), blood type B (BB and BO), and blood type O (OO).
User Queries
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
How do I create a Punnett square for an independent practice scenario?
List the alleles of one parent along the top of the square and the alleles of the other parent along the side. Fill in the squares with the possible combinations of alleles.
Why are Punnett squares important?
Punnett squares help us understand the probability of inheriting certain traits and can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses.