Embark on an illuminating journey into the realm of protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet, where we delve into the intricacies of protein production, unraveling the fundamental processes that govern the building blocks of life. This comprehensive guide, crafted with academic rigor and authoritative tone, promises an immersive exploration of protein synthesis, empowering you with a profound understanding of this essential biological mechanism.
Protein Synthesis Overview: Protein Synthesis And Amino Acid Worksheet
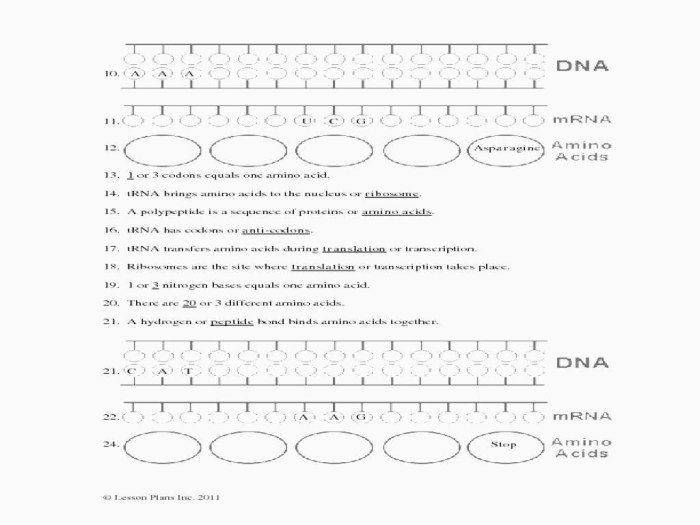
Protein synthesis is the fundamental process by which cells create proteins, essential molecules for cellular structure and function. Proteins are composed of amino acids, which are linked together in a specific sequence determined by the genetic code.
Protein synthesis plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, including metabolism, growth, cell division, and signaling. It ensures the proper functioning and maintenance of cells and organisms.
Transcription and Translation
Protein synthesis involves two main stages: transcription and translation.
Transcriptionoccurs in the nucleus, where DNA is used as a template to create messenger RNA (mRNA). RNA polymerase, an enzyme, facilitates the transcription process.
Translationtakes place in the cytoplasm, where mRNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid, interact with mRNA to form a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes, cellular structures, facilitate the translation process.
The flow of genetic information during protein synthesis is: DNA → mRNA → Protein.
Amino Acid Structure and Properties
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. They consist of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group).
The genetic code specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Each amino acid has a unique side chain, contributing to the protein’s structure and function.
Protein Folding and Function, Protein synthesis and amino acid worksheet
After translation, proteins undergo a process called folding, which determines their final shape and function.
Protein folding occurs in stages, resulting in four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
The relationship between protein structure and function is crucial. The specific shape of a protein enables it to interact with other molecules and perform its specific role in cellular processes.
Protein Synthesis Regulation
Protein synthesis is tightly regulated to ensure that the correct proteins are produced at the right time and in the right amounts.
Transcription factors and other regulatory proteins play a key role in regulating protein synthesis by controlling the initiation, elongation, and termination of transcription and translation.
Regulation of protein synthesis is essential for cellular homeostasis and response to environmental cues.
Applications of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis has numerous applications in biotechnology and medicine.
Recombinant DNA technologyallows scientists to produce proteins of interest for research, therapeutic, and industrial purposes.
Protein synthesis is also crucial in drug development and disease treatment, enabling the production of therapeutic proteins, such as antibodies and enzymes, to target specific diseases.
FAQ
What is the role of amino acids in protein synthesis?
Amino acids serve as the building blocks of proteins, linked together in specific sequences to form polypeptide chains.
How does transcription differ from translation in protein synthesis?
Transcription involves copying the genetic code from DNA into mRNA, while translation converts the mRNA code into a sequence of amino acids.
What factors regulate protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis is regulated by various mechanisms, including transcription factors, regulatory proteins, and cellular signaling pathways.


