Boyle’s law and charles law gizmo – Unveiling the intricacies of gas behavior, this exploration delves into Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law, utilizing the interactive “Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law Gizmo” simulation. Through a captivating journey, we will unravel the inverse relationship between pressure and volume, the direct relationship between temperature and volume, and the combined effects of these variables on gas properties.
Embark on this scientific adventure to gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles governing gases.
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. According to this law, when the pressure of a gas increases, its volume decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:P1V1 = P2V2where P1 and V1 represent the initial pressure and volume, and P2 and V2 represent the final pressure and volume.Boyle’s
Law has numerous applications in real-life situations, such as:
- The operation of scuba diving equipment, where Boyle’s Law is used to calculate the depth at which a diver can safely ascend without experiencing decompression sickness.
- The design of airbags in cars, which inflate rapidly upon impact to increase the volume and decrease the pressure inside the vehicle, cushioning the occupants.
- The manufacturing of plastic bottles, which are often filled with gas to a certain pressure, and the volume of the bottle changes as the pressure inside changes due to temperature fluctuations.
| Boyle’s Law | Charles’ Law |
|---|---|
| Inverse relationship between pressure and volume | Direct relationship between temperature and volume |
| P1V1 = P2V2 | V1/T1 = V2/T2 |
| Applies at constant temperature | Applies at constant pressure |
Charles’ Law

Charles’ Law describes the direct relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure. According to this law, when the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:V1/T1 = V2/T2where V1 and T1 represent the initial volume and temperature, and V2 and T2 represent the final volume and temperature.Charles’
Law has important implications for understanding gas behavior in different environments, such as:
- The expansion of gases in hot air balloons, which causes them to rise due to the increased volume of the heated air inside.
- The design of thermometers, which rely on the expansion and contraction of a gas (such as mercury or alcohol) to indicate temperature changes.
- The behavior of gases in weather patterns, where changes in temperature can affect the volume and pressure of air masses, leading to weather phenomena like updrafts and downdrafts.
To demonstrate Charles’ Law, a simple experiment can be designed using common household materials:
- Fill a balloon with a small amount of air.
- Tie the balloon closed and place it in a refrigerator or freezer for several hours.
- Remove the balloon from the refrigerator and observe its size.
- Gently warm the balloon using a hair dryer or by placing it in a warm environment.
- Observe the changes in the balloon’s size as it warms up.
The experiment demonstrates that as the temperature of the air inside the balloon decreases, its volume decreases, and as the temperature increases, its volume increases, supporting Charles’ Law.
Combined Gas Law: Boyle’s Law And Charles Law Gizmo
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law to describe the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas under varying conditions. It is expressed mathematically as:P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2This equation can be derived by combining the equations for Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law:P1V1 = P2V2 (Boyle’s Law)V1/T1 = V2/T2 (Charles’ Law)Multiplying these equations, we get:P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 (Combined Gas Law)The Combined Gas Law allows us to predict the changes in pressure, volume, or temperature of a gas when any two of these variables change.
| Variable | Relationship |
|---|---|
| Pressure (P) | Inversely proportional to volume (V) at constant temperature |
| Volume (V) | Directly proportional to temperature (T) at constant pressure |
| Temperature (T) | Directly proportional to volume (V) at constant pressure |
Gizmo Simulation
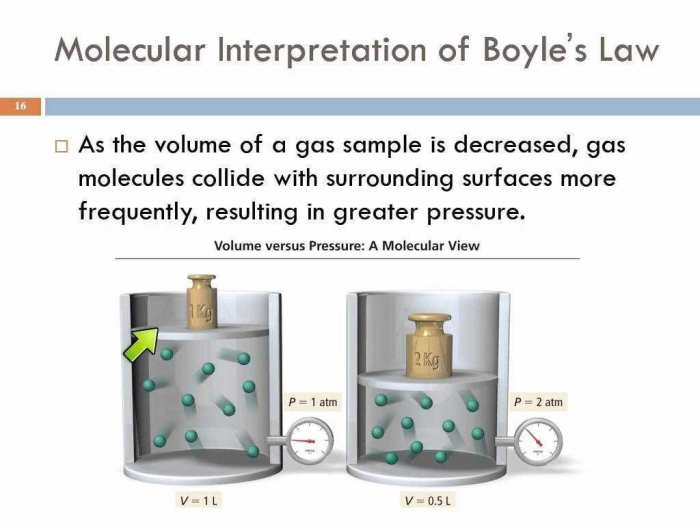
The “Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law Gizmo” simulation provides a virtual environment for investigating the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. The simulation allows users to manipulate these variables and observe the corresponding changes in the gas’s behavior.The
Gizmo features:
- A gas chamber with adjustable volume and pressure
- A temperature gauge
- Real-time graphs displaying the changes in pressure, volume, and temperature
Using the Gizmo, users can:
- Investigate the inverse relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature (Boyle’s Law)
- Explore the direct relationship between temperature and volume at constant pressure (Charles’ Law)
- Combine Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law to understand the Combined Gas Law
The Gizmo provides an interactive and engaging way to learn about gas laws and their applications in real-world scenarios.
Real-World Applications
Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Engineering:Designing engines, compressors, and other devices that involve gas compression or expansion.
- Chemistry:Determining the volume or pressure of gases in chemical reactions and industrial processes.
- Meteorology:Predicting weather patterns by understanding the behavior of gases in the atmosphere.
Specific examples include:
- Using Boyle’s Law to calculate the pressure changes in scuba diving tanks as divers ascend or descend.
- Applying Charles’ Law to design hot air balloons that can achieve a desired altitude by controlling the temperature of the air inside.
- Combining Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law to understand the expansion and contraction of gases in weather systems, which can help predict the formation of clouds, storms, and other weather phenomena.
Understanding Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law is crucial for solving practical problems and advancing our knowledge of the behavior of gases in various contexts.
FAQ Corner
What is Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature.
How does Charles’ Law relate to Boyle’s Law?
Charles’ Law describes the direct relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure.
What is the Combined Gas Law?
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law to relate pressure, volume, and temperature changes of a gas.
How can the “Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law Gizmo” simulation help me?
The simulation allows you to visualize and experiment with the effects of changing pressure, volume, and temperature on gases.